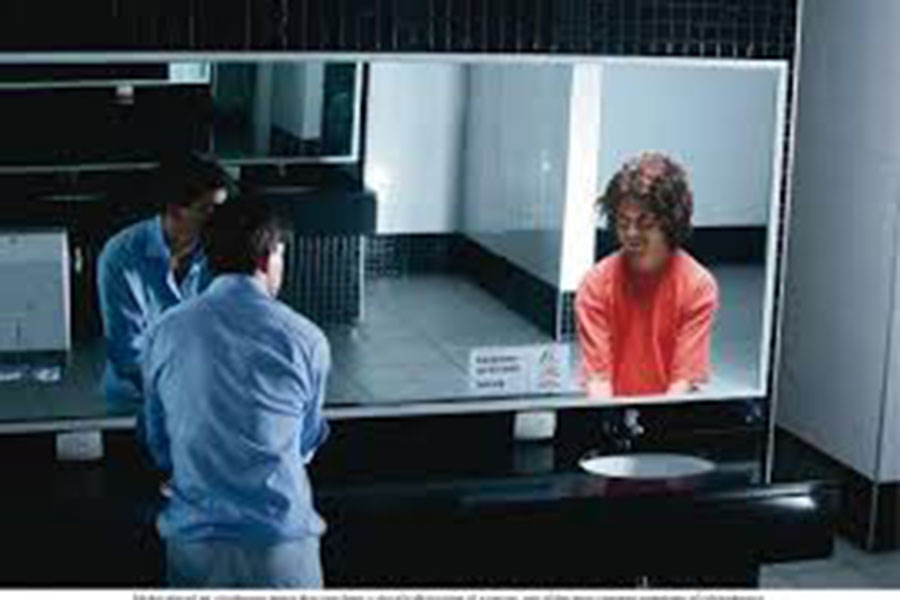
There is currently no diagnostic test for schizophrenia. The age of onset is usually between the late teens and early thirties. Diagnosis is based on an individual’s history and presenting symptoms. Positive, negative and cognitive symptoms are identified. Positive symptoms are delusions and hallucinations. Sometimes people confuse these two symptoms. A delusion is a belief that is not based in reality. In the scenario presented, the individual believed that he was an undercover FBI agent. Delusionsoften have themes involving religion, sex or the government. An individual who has schizophrenia may have paranoid delusions, believing that a person or group will harm him/her. Hallucinations involve the senses. They can be auditory, visual, tactile, olfactory or gustatory. The most common are auditory hallucinations, sometimes referred to as “voices.” An individual who is hearing voices may appear distracted, be slow to respond or appear to be listening or laughing inappropriately. Initially the voices can be comforting or amusing but this changes as the disease progresses. The voices can become very critical and derogatory.
This month’s civil & criminal topic is Schizophrenia. Topics covered are:
- Case Scenario (8/4/14)
- Symptoms and Diagnosis (8/11/14)
- Approach Considerations (8/18/14)
- Medical Treatment Options (8/25/14)
Note: To see all posts in this topic, click here