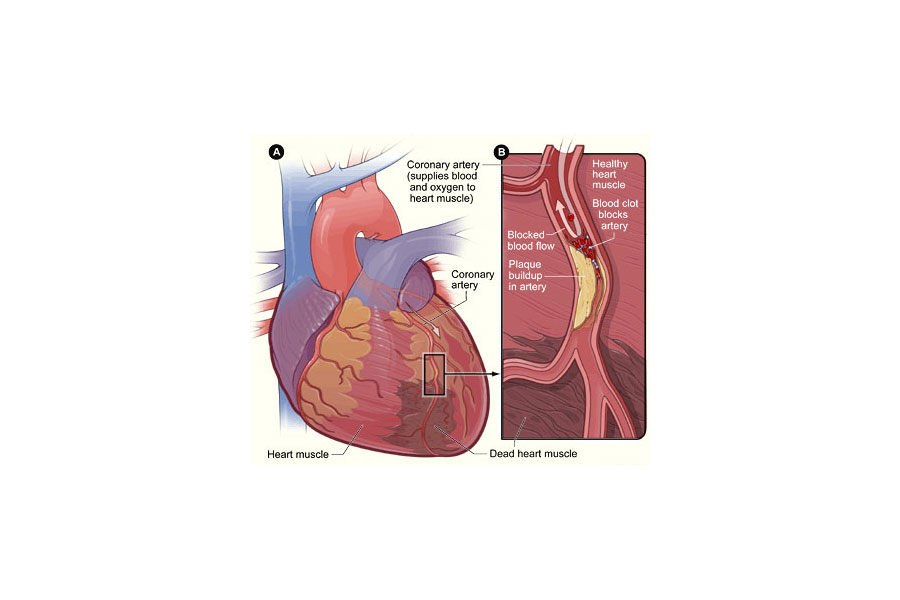
The medical term for heart attack is Myocardial Infarction. “Myocardial” is the heart muscle and “infarction” is cell death:
There are 4 main coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart and allow it to pump blood out to the body. When these coronary arteries become clogged there is ischemia, or insufficient blood flow. In this case, the cells may still work, but not as well. Or there may be enough of their friends around them to function. But the patient may experience the symptoms of a heart attack such as nausea, chest pain, or shortness of breath. They experience these symptoms because the body is telling them that it’s not getting enough blood to that area and something is wrong with the heart.
If the blockage is significant enough and the cells don’t get the nutrients they need for a period of time, the cells die and this is called infarction. Once the cells die it is not reversible, which is why it is so important to treat the underlying cause of the ischemia before the infarction occurs.
When you hear about someone having a “CABG” or “triple bypass surgery,” these are surgical operations performed to create a new path and bypass the coronary arteries that are blocked. CABG is a Coronary Artery Bypass Graft; and the triple means that three coronary arteries had to be bypassed due to the inability to remove the blockage.
This month’s civil topic is heart attacks as a missed diagnosis in medical malpractice cases. Topics covered are:
- What is a heart attack? (5/5/14)
- Statistics on heart attacks (5/12/14)
- Physician responsibility and risk factors (5/19/14)
- Legal implications (5/26/14)
Note: Links won’t work until the date posted.